Introduction
GrayLog is a powerful open source SIEM solution. With hosting within Azure there was additional parameters that needed to be changed to get it to work. If you are testing the solution is might be worth using a site such as azureprice.net to find the best price based on the location and your size requirements.
Specification Used
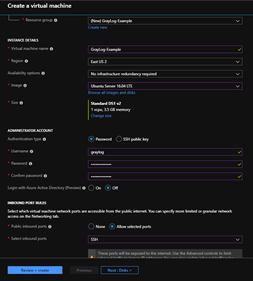
OS: Ubuntu Server 16.04 LTS
Size: Standard DS1 v2 (1 vcpu, 3.5 GB memory)
Location: East US 2
Additional Disk: 50GB
The price an hour for this set up came to 0.07
Networking Config
Below are the Inbound Port rules for the GrayLog instance.
| Order | Name | Port | Protocol | Source | Destin | Action | |
| 101 | Graylog_web_interface | 9000 | Any | Any | Any | Allow | … |
| 102 | Elasticsearch | 9200 | Any | Any | Any | Allow | … |
| 103 | Elasticsearch_node_communication | 9300 | Any | Any | Any | Allow | … |
| 104 | MongoDB | 27017 | Any | Any | Any | Allow | … |
| 105 | graylog_rest_api | 12900 | Any | Any | Any | Allow | … |
| 106 | filebeats | 5044 | Any | Any | Any | Allow | … |
| 340 | SSH | 22 | TCP | Any | Any | Allow | … |
Configuring GrayLog
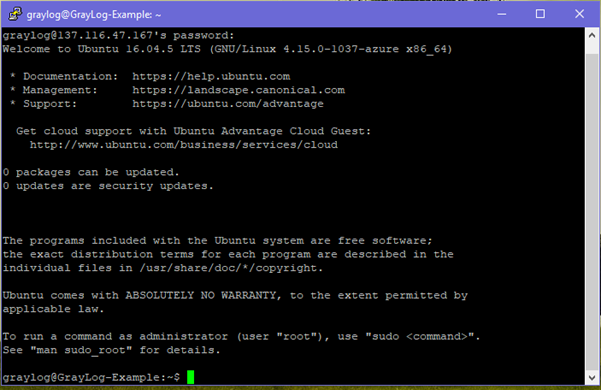
Once set up SSH into the VM
First update the system:
sudo apt-get update && sudo apt-get -y upgradeInstall Java 8 onto the system
sudo apt-get install software-properties-common
sudo apt-add-repository ppa:webupd8team/java
sudo apt-get update
sudo apt install oracle-java8-installer
java -version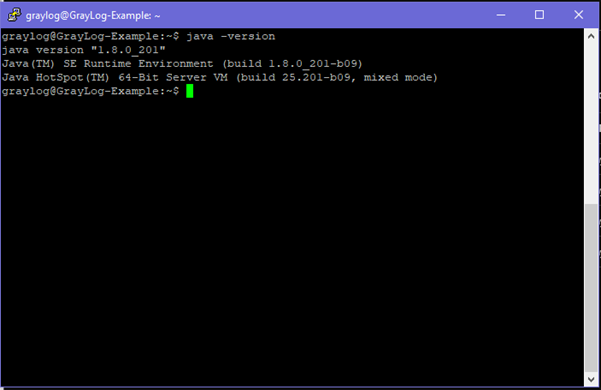
Installing MongoDB
sudo apt-key adv --keyserver hkp://keyserver.ubuntu.com:80 --recv 7F0CEB10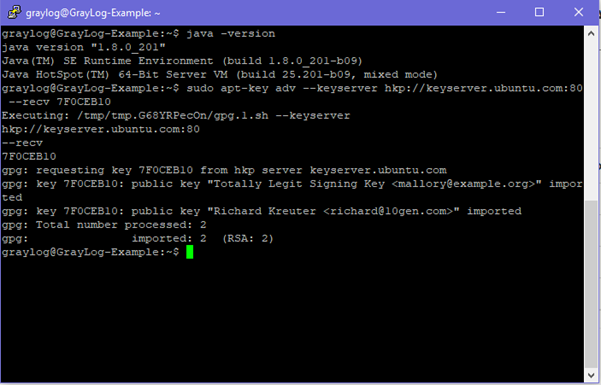
sudo echo "deb http://repo.mongodb.org/apt/debian wheezy/mongodb-org/3.0 main" > /etc/apt/sources.list.d/mongodb-org-3.0.list
apt-get update
sudo apt-get install mongodb-orgEnable MongoDB to start on reboot
systemctl enable mongodStart MongoDB
systemctl start mongodCheck the status of MongoDB, ensure it’s started
systemctl status mongod 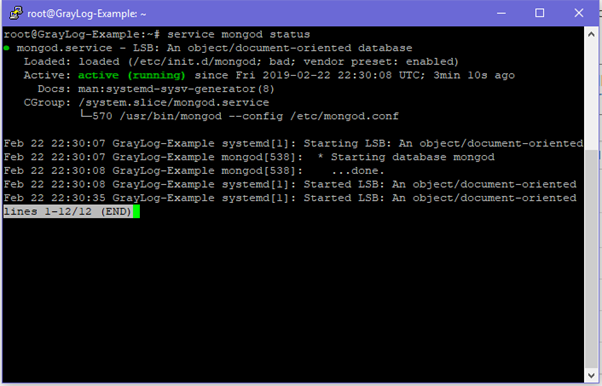
Installing Elastic Search:
wget -qO - https://packages.elastic.co/GPG-KEY-elasticsearch | sudo apt-key add –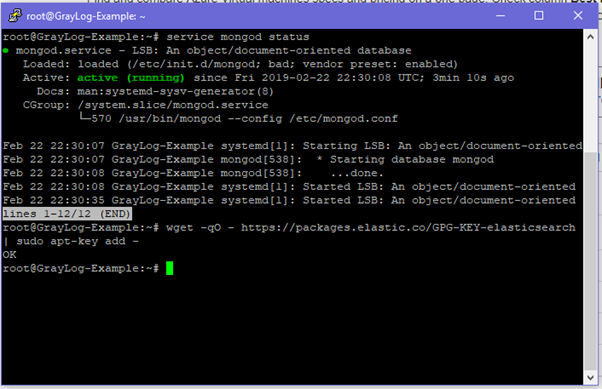
apt-get install apt-transport-httpsecho "deb https://packages.elastic.co/elasticsearch/2.x/debian stable main" | sudo tee -a /etc/apt/sources.list.d/elasticsearch-2.x.list
apt-get update && apt-get install elasticsearchEdit the elasticsearch.yml file and change the cluster name:
nano /etc/elasticsearch/elasticsearch.yml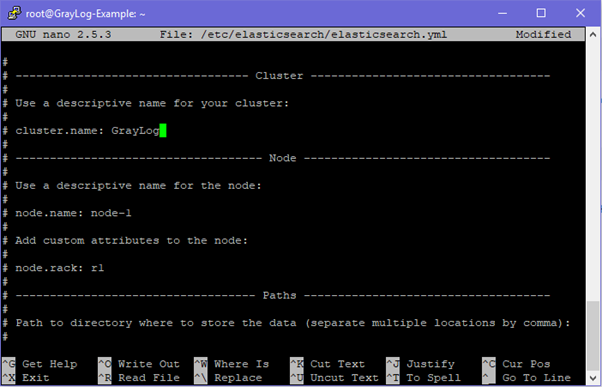
Start and enable elastic search
systemctl start elasticsearch
systemctl enable elasticsearch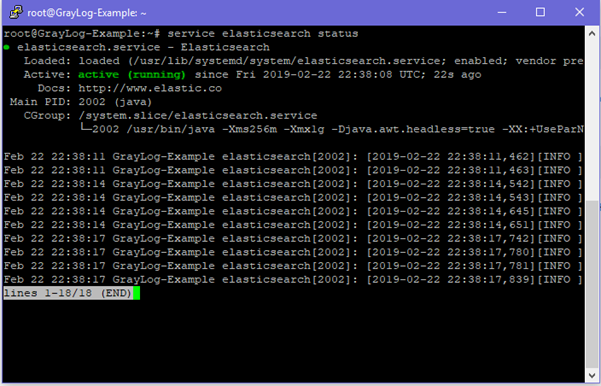
Installing GrayLog:
wget https://packages.graylog2.org/repo/packages/graylog-2.3-repository_latest.deb
dpkg -i graylog-2.3-repository_latest.deb
apt-get update && apt-get install graylog-serverNext, you’ll need to generate a hash password for the root user (which you only need to initially set up the system and in case you lose connectivity to your authentication backend). This will be the value for the root_password_sha2 variable.
echo -n yourpasswordhere | sha256sum
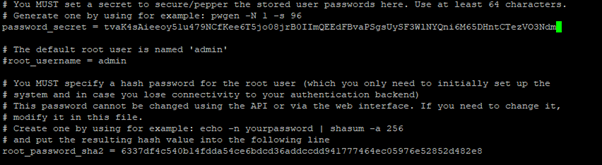
6337df4c540b14fdda54ce6bdcd36addccdd941777464ec05976e52852d482e8Next you’ll need to generate a secret to secure/pepper the stored user passwords. This will be the value for the password_secret variable.
apt-get install pwgen
pwgen -s 80 1 tvaK4sAieeoy51u479NCfKee6T5jo08jrB0IImQEEdFBvaPSgsUySF3WlNYQni6M65DHntCTezVO3NdmRun the below command to find the private IP address of the system
ip route get 8.8.8.8 | awk '{print $NF; exit}'
10.0.2.4Finally get the public address of the system
137.116.47.167root@graylog:~# –

Edit the server.conf file for GrayLog:
nano /etc/graylog/server/server.confChange the following variables to the earlier created values:
- password_secret
- root_password_sha2
Next change the following variables:
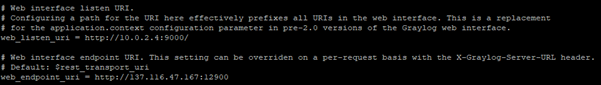
- rest_listen_uri = http://<your.private.ip.addr>:12900
- web_listen_uri = http://<your.private.ip.addr>:9000
- web_endpoint_uri = http://<your.public.ip.addr>:12900

Once edited save the server.conf file and start and enable GrayLog:
systemctl enable graylog-server.service
systemctl restart graylog-server.service
Next browse to GrayLog from a web browser:
http://<your.public.ip.addr>:9000
Login using the account ‘admin’ and the password set up earlier:
In the next guide we’ll walk through setting up FileBeat as our log collectors for the GrayLog Server.
Using FileBeat with GrayLog
Set up a new ‘Beats’ input in GrayLog. Enter a Title and ensure the port to listen on is 5044.
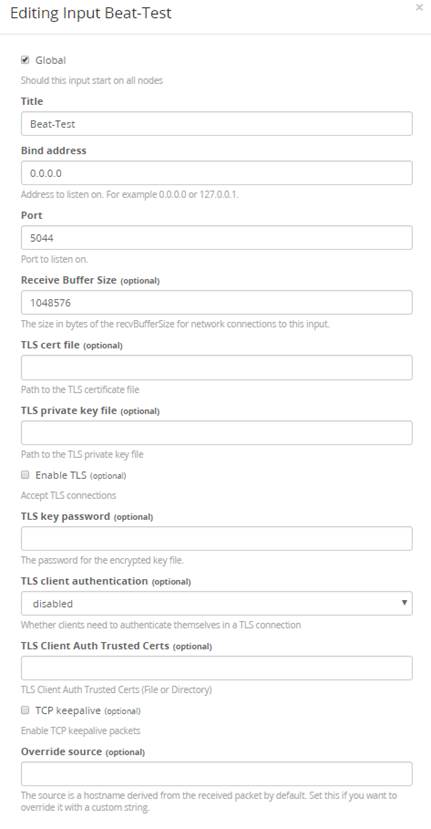
Installing File Beat
APT
To add the Beats repository for APT:
Download and install the Public Signing Key:
wget -qO - https://artifacts.elastic.co/GPG-KEY-elasticsearch | sudo apt-key add -You may need to install the apt-transport-https package on Debian before proceeding:
sudo apt-get install apt-transport-httpsSave the repository definition to /etc/apt/sources.list.d/elastic-6.x.list:
echo "deb https://artifacts.elastic.co/packages/6.x/apt stable main" | sudo tee -a /etc/apt/sources.list.d/elastic-6.x.listRun apt-get update, and the repository is ready for use. For example, you can install Filebeat by running:
sudo apt-get update && sudo apt-get install filebeatTo configure Filebeat to start automatically during boot, run:
sudo update-rc.d filebeat defaults 95 10YUM
To add the Beats repository for YUM:
Download and install the public signing key:
sudo rpm --import https://packages.elastic.co/GPG-KEY-elasticsearchCreate a file with a .repo extension (for example, elastic.repo) in your /etc/yum.repos.d/directory and add the following lines:
[elastic-6.x]
name=Elastic repository for 6.x packages
baseurl=https://artifacts.elastic.co/packages/6.x/yum
gpgcheck=1
gpgkey=https://artifacts.elastic.co/GPG-KEY-elasticsearch
enabled=1
autorefresh=1
type=rpm-mdYour repository is ready to use. For example, you can install Filebeat by running:
sudo yum install filebeatTo configure the Beat to start automatically during boot, run:
sudo chkconfig --add filebeatConfiguring File Beat
Edit the filebeat.yml config file:
nano /etc/filebeat/filebeat.ymlUnder filebeat.inputs enter the paths for the logs that will be pushed to GrayLog
#=========================== Filebeat inputs =============================
filebeat.inputs:
# Each - is an input. Most options can be set at the input level, so
# you can use different inputs for various configurations.
# Below are the input specific configurations.
- type: log
# Change to true to enable this input configuration.
enabled: true
# Paths that should be crawled and fetched. Glob based paths.
paths:
- /var/log/*.log
Next edit the Logstash output host variable:
#----------------------------- Logstash output --------------------------------
output.logstash:
# The Logstash hosts
hosts: ["137.116.47.167:5044"]
# Optional SSL. By default is off.
# List of root certificates for HTTPS server verifications
#ssl.certificate_authorities: ["/etc/pki/root/ca.pem"]
# Certificate for SSL client authentication
#ssl.certificate: "/etc/pki/client/cert.pem"
# Client Certificate Key
#ssl.key: "/etc/pki/client/cert.key"Start and enable File Beat
systemctl enable filebeat
systemctl restart filebeat
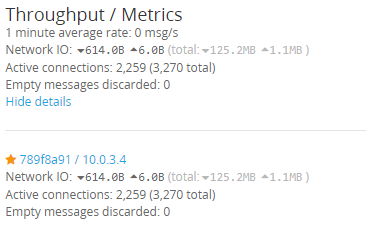
Going back to the inputs you should start seeing Network IO. Logs should start appearing into Graylog.